Characteristics of Coal
The sulfur volatile substance contains is the basic features that determine the quality of coal.
Classification of Coal
Coal is widely used for heating with energy and electricity production in industry due to its easy -to -find and regular change in prices. Coal quality is determined according to the purpose of use.
Although the classification of coal varies depending on the source, it is similar to each other. The basic classification is made on the heater value of coal.
The anthracite coals are divided into three sub-groups as "meta-authusitis", "anthracite" and "semi-antrasyite" in itself according to the fixed C and volatile ratio contained in the form of heating values the same.
Breaking of coal
After the production of coal is produced well in order to be well cleaned from the impurities in it.
The crusher type to be used for breaking coal varies according to the amount of coal to be broken, the structure of the coal, the desired size after breaking. It is specially manufactured for coal breaking.
Figure 6 shows the only roller (Dresser) and hammer crusher (Pennsylvania Crusher Corp.) used in the breakage of coal.
With the hammer crushers in the figure, coke can make coal under 3 mm to raise less dust up to -100 µ. The crusher rotor can work in two ways, the distance between the plates in the body and the hammer on the rotor can be adjusted. These crushers also have the possibility to grind under -100 µ -100 µ.
Figure 7 shows the coal breaking mills called Bradford and Bradpactor.
In Bradford coal crushers, coal made from the stove is broken and dimensioned, and less fragile parts without coal are cleaned. In these crushers, the sieve-shaped body turns with a speed of 12-14 cycles, while the pallets in the crusher raise the material to be broken and the material falls down from a certain height with its own weight. While the broken material is sieved in the sieve size that forms the body, less fragile materials without coal are separated from the crushing mouth and separated from the coal. The sieve is changed as these crushers wear. Crushers also have the possibility to use sieves in the desired opening. The life of the crushers is quite long.
In Bradpactor coal crushers, a rotating shaft with a rolle palette is placed on the inner center of the body. This shaft, which can be replaced by the speed, turns in the opposite direction and the coal in the crusher is broken. By changing the rotational speed of the shaft in the crusher, the crushing size and crushing capacity can be adjusted.
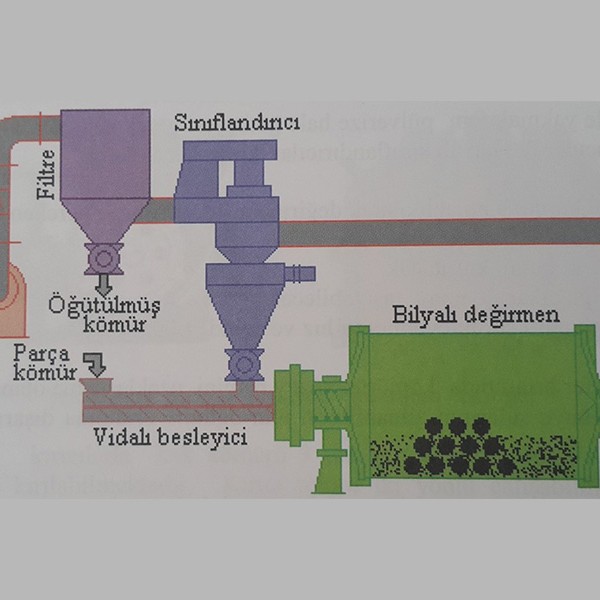
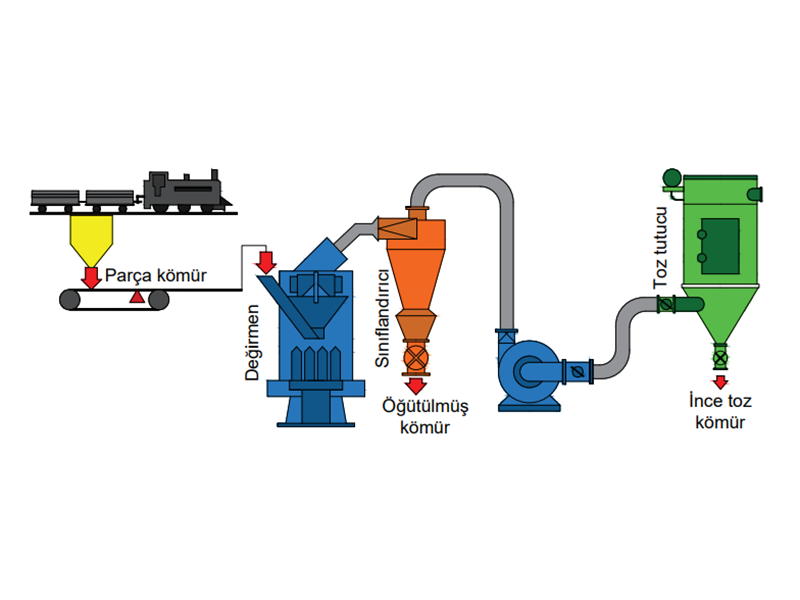
Grinding of coal
To burn the coal with a burner, it is required to make it pülverized. In the grinding, ball and roll mills and cool classifications are used.
Air amount to be sent to the mill for drying purposes in coal grinding:
It will dry the moisture in coal,
Can carry the moisture that will be revealed in the environment,
The speed and flow that can drag ground coal should be.
In an appropriate atmosphere environment, coal has the possibility to remove the surface moisture. However, in order to obtain the capillary waters of coal, external heat should be given to the grinding environment.
The temperature of the air from the mill is 15-20 ° C higher than the temperature in which the coal leaves the moisture in the mill. The required temperature values in grinding are converted to graph. For example, if the exit air temperature in a mill operating under appropriate conditions is 70 ° C, the moisture of coal containing 10 %moisture in the mill is moving away from the structure of around 55 ° C. Under these conditions, the air temperature given to drying mills must be approximately 350 ° C. The air temperature should not be increased on this value.
When the mill is given air for drying at a temperature of 300 ° C, 1.2kg air per ton is required to dry the coal containing less than 10 %moisture.
The drying atmosphere and temperature required for drying a coal containing 5-30 %moisture, which is fed to the mill at 10 ° C in graph 1, is shown in graphically. (UTM)
When the drying air temperature was 300 ° C for drying of a coal containing 10 %moisture of the observations, 1.5kg air for 1kg of coal and 2.0kg air in rolls with rolls were required.
The coal mill returns to the desired size in the circuit. The capacity of the circuit decreases when the machines in the grinding circuit and the coal size fed to grind are not selected correctly.
In the grinding of coal, ball, waltzed, rolls, pendulums, jet mills are used, and for size control, the mills are run with different classes. The grinder mill is selected according to operating costs such as first investment, labor, power, maintenance, the type of material to be grinded and the necessary grinding environment.
It can be burned with burners below -300 µ according to coal quality. For a good combustion, the coal should be grinded with a maximum of 100 µ sieve, and for an ideal combustion to be d80 = -75 µ, the fine surface area of the specific surface area can burn faster. Finely ground coal tends to burn self and causes the sulfur and humidity coal stocks to be burned by an internal oxidation.
Ball mills are expensive for grinding, difficult to assemble. These mills have low grinding and drying capacity compared to other mills. It is difficult to interrupt the relationship between the grinding environment with the environment and to maintain my leakage. It gives good results in the grinding of coals with a hard grove index with ball mills higher than 30.
Very good size control is achieved when perpendicular rolled and pendulum mills are operated with dynamic classifications. Grinding activity and drying capacity are higher than the ball mills. These mills have the opportunity to operate for 1-2 years with ordinary maintenance after good care.
Grinding of Coal: Hardgrove method